User Guide
Installing CloudNatix to Kubernetes Clusters
Prerequisites
General:
- Cluster Controller pods running in K8s clusters need to be able to send HTTPS requests to the Internet (e.g., api.cloudnatix.com).
- Support Kubernetes version 1.21 and above.
AKS only:
- Cluster Controller requires read-only access to Azure resources. To grant the role to Cluster Controller pods, either Azure Active Pod Identity or Azure Active Directory pod-managed identity needs to be configured. See Appendix A, Appendix B, and Appendix C for the details.
EKS only:
- K8s Metrics Server needs to be installed. See Installing the Kubernetes Metrics Server for the installation procedure.
- The minimum K8s cluster size is 2
t3.mediumworker nodes. - IAM role for the cluster requires the
ec2:Describe*permission or theAmazonEC2ReadOnlyAccesspolicy. See Appendix D if the cluster is using IAM roles for service accounts (IRSA). If IRSA is not used and IMDSv2 is enabled, the hop-limit of PUT responses must be set to 2. See the AWS document for more details. Please note that changing the hop-limit is not allowed in the EKS Auto mode (issue).
GKE only:
- The
cluster-watcherdeployment in thecloudnatixnamespace needs to be associated with the service account that has a role ofKubernetes Engine Cluster ViewerandCompute Viewer. See Appendix E for the details.
OKE only:
Please use one of the following methods to grant cluster-watcher deployment in the cloudnatix namespace to access OCI resources:
- associate
cluster-watcherdeployment with an OCI user, See Appendix F for the details. - associate
cluster-watcherdeployment with an OCI workload identity policy, See Appendix G for the details.
KIND only:
- The minimum KIND cluster size is 1 node with 2 cores and 16GB.
Installation Procedure
This section describes the procedure for installing Cluster Controller to a target Kubernetes cluster. Cluster Controller components are deployed to the cloudnatix namespace and connect to Global Controller to provide features such as workload visibility and optimization.
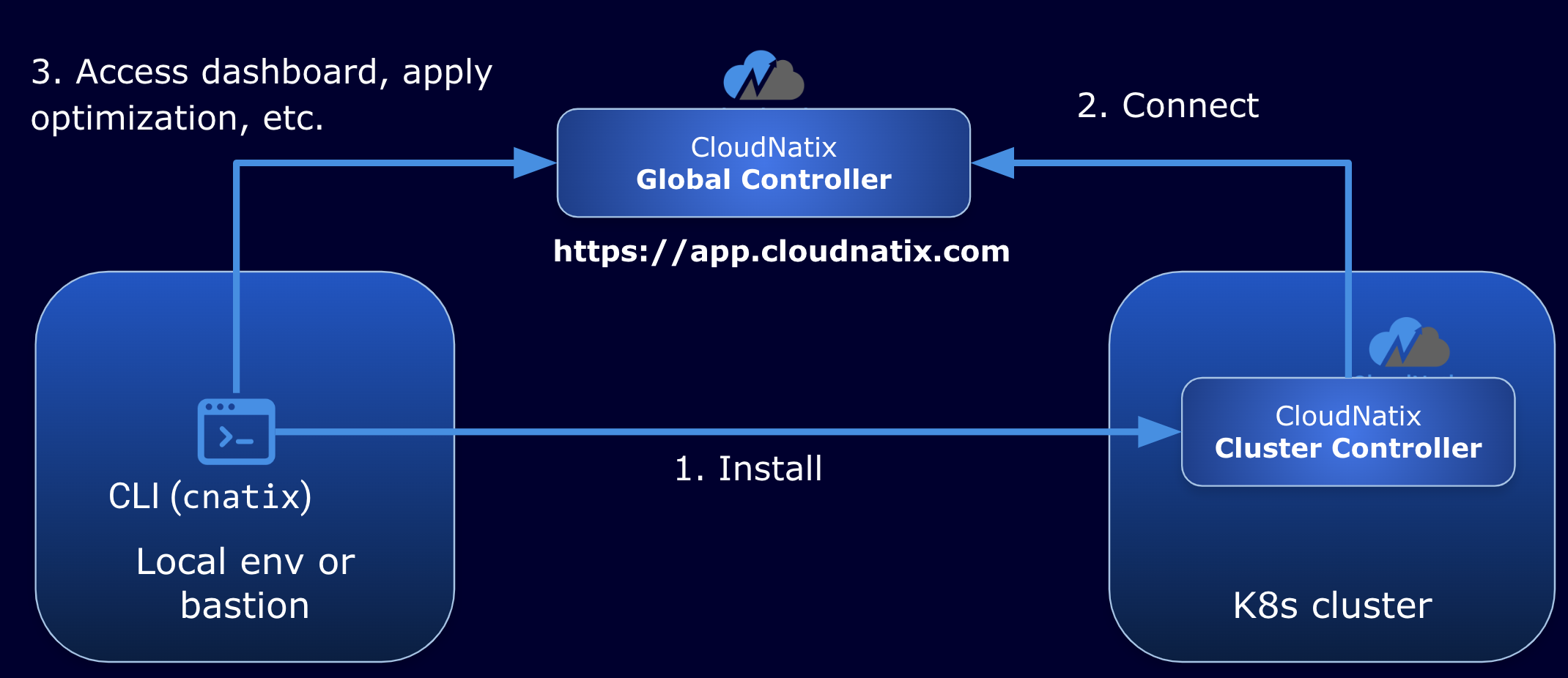
Step 1. Download the CLI
Please obtain the latest version of the CLI (cnatix) from either the CloudNatix web UI, or by following the instructions in Appendix K. Note that the download link expires in 1 hour. There's a button named "Install CLI" on the side menu bar. Select version 21.2 and channel stable.
Step 2. Set up CSP credentials (for AKS, EKS and GKE)
Please set environment variables to be able to issue (readonly) API calls to CSP. It is necessary to obtain the configuration of K8s clusters during the installation process.
For AKS, run the following command to verify:
az aks list
For EKS, run the following command to verify:
aws eks list-clusters
For GKE, run the following command to verify:
gcloud container clusters list
For OCI, run the following command to verify:
oci ce cluster list --compartment-id <compartment-ocid>
Step 3. Set the current kubeconfig context
Please also set the context of the kubeconfig to an K8s cluster where Cluster Controller is installed.
For AKS, run the following command to generate a kubeconfig:
az aks get-credentials --resource-group <resource group> --name <cluster name>
For EKS, run the following command to generate a kubeconfig
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region <region> --name <cluster name>
For GKE, run the following command to generate a kubeconfig:
gcloud container clusters get-credentials <cluster name>
For OKE, run the following command to generate a kubeconfig:
oci ce cluster create-kubeconfig \
--cluster-id <your cluster OCID> \
--file <file path of kubeconfig> \
--region <region-name>
Step 4. Generate a YAML file and a Helm chart for installing Cluster Controller
First type cnatix login to login CloudNatix.
$ cnatix login
Type cnatix clusters configure and answer questions. When all questions are answered, a YAML file and a Helm chart for installing Cluster Controller is generated under ~/.cnatix/cluster-configs/<cluster-name>.
Note: Currently, only the admin of the root org can run this command. Please contact CloudNatix if you want to delegate this operation to non-root-admin users.
$ cnatix clusters configure
Welcome! This command will guide you through configuring install parameters.
Initializing... done
? Use current context(my-cluster) to install? Yes
- configuring AKS my-cluster cluster...
? Choose CloudNatix distribution version: 21.2
? Choose CloudNatix channel: stable
? Enable CloudNatix components auto-upgrade? Yes
? Send Kubernetes container arguments and environment variables to global controller? Yes
Writing the configuration file... done
Successfully configured install parameters!
Please run ANY of the following command to install CloudNatix Cluster Controller:
[Use cnatix CLI]: cnatix clusters install --name=my-cluster
[Use YAML file ]: kubectl apply -f /home/user/.cnatix/cluster-configs/my-cluster/ccoperator.yaml
[Use Helm Chart]: helm install -n cloudnatix --create-namespace ccoperator /home/user/.cnatix/cluster-configs/my-cluster/ccoperator
Please set the distribution to 21.2 and the channel to stable.
Note: Please note that this Helm chart includes a secret that contains an API key. If you want to avoid embedding the API key in the chart, please remove the following from the Helm chart:
apiKeyanddockerconfigjsonfromvalues.yamlsecret.yaml
Please see Appendix H for the details.
Note: We will install Prometheus Operator if the target cluster hasn’t it yet. If the target cluster already has Prometheus, we will not install an additional instance. You will see a message like below:
? Choose Prometheus to use for CloudNatix: [Use arrows to move, type to filter]
> cloudnatix/kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus - existing
cloudnatix/prometheus-operated - existing
<create>
Note: If you want to run Cluster Controller pods to specific nodes, please answer the following questions and set a target node label and/or a toleration.
? Input a node selector in key=value format: (end if empty)
? Input a toleration key: (end if empty)
Note: CloudNatix Cluster Controller sends the spec of Kubernetes resources to Global Controller to display the information in Dashboard. Please type n to the following question if you want to remove commandline arguments or environment variables in spec information sent to Global Controller:
? Send Kubernetes container arguments and environment variables to global controller? [? for help] (y/n)
Note: For GKE clusters, the configure command has an additional question for configuring Workload Identity Federation.
Following is a sample prompt on setting up a user profile for CloudNatix Cluster Controller.
? Input service account: cloudnatix@cloudnatix-dev.iam.gserviceaccount.com
See Appendix E for how to create the service account.
Note: For OKE clusters, the configure command has additional questions for configuring workload identity or user profile.
Following is a sample prompt on setting up a user profile for CloudNatix Cluster Controller.
? Use workload identity? No
? Use user OCID ocid1.user.**** for cloudnatix workload? No
? Input user configuration file path: <file path to the user configuration file>
? Input user profile name: DEFAULT
? Input the password if user private key is encrypted:
Following is a sample prompt on setting up workload identity for CloudNatix Cluster Controller.
? Use workload identity? Yes
Step 5. Apply the YAML file or install the Helm chart
Apply the generated YAML file by running kubectl apply -f or install the Helm chart.
You will see pods created in the cloudnatix namespace.
$ kubectl get pods -n cloudnatix
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
authtokenrefresher-654654bfdb-q875k 1/1 Running 0 65s
ccoperator-6896f487c6-xqdrh 1/1 Running 0 87s
cluster-watcher-69ddbdb7d6-qd2xr 1/1 Running 0 54s
clusteragent-7bc457c548-449xh 1/1 Running 0 63s
connect-agent-69585c4995-dlq8s 2/2 Running 0 67s
infra-operator-7d7b768c7d-9lvm2 1/1 Running 0 49s
vpa-admission-controller-6489c786d7-24xcc 1/1 Running 0 56s
vpa-recommender-67f6f6f998-hgthh 1/1 Running 0 56s
vpa-updater-55496cc648-p48vj 1/1 Running 0 56s
The Workloads page will show a list of workloads in the cluster.
Uninstallation Procedure
Please type cnatix clusters uninstall --name <cluster-name>.
When this command runs, the ccoperator pod must be running as the pod orchestrates the uninstallation process (e.g., uninstall Cluster Controller components installed by ccoperator, delete CRDs).
Please note that the context of the kubeconfig must not be set to the one that is generated by CloudNatix. If the context is set to the CloudNatix generated one, the uninstallation won't successfully complete (as k8s API server becomes unreachable from the uninstallation process in the middle of uninstallation).
Please avoid just deleting the cloudnatix namespace as it will not unregister the cluster from Global Controller.
If you no longer have ccoperator in your Kubernetes cluster or you have deleted the Kubernetes cluster, you can also run cnatix clusters unregister to delete the cluster from CloudNatix dashboard.
Appendix A: Enabling Azure Active Directory Pod Identity
Please follow Getting Started to install AAD Pod Identity if you haven’t.
Here are example commands for the installation and role assignment.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/aad-pod-identity/master/deploy/infra/deployment-rbac.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/aad-pod-identity/master/deploy/infra/mic-exception.yaml
export CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP=<resource group of the cluster>
export CLUSTER_NAME=<cluster name>
export KUBELET_IDENTITY_ID=$(az aks show -g ${CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP} -n ${CLUSTER_NAME} --query identityProfile.kubeletidentity.clientId -o tsv)
export NODE_RESOURCE_GROUP="$(az aks show -g ${CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP} -n ${CLUSTER_NAME} --query nodeResourceGroup -o tsv)"
export NODES_RESOURCE_ID=$(az group show -n ${NODE_RESOURCE_GROUP} -o tsv --query "id")
# Assign the roles to the Kubelet identity.
az role assignment create --role "Managed Identity Operator" --assignee ${KUBELET_IDENTITY_ID} --scope ${NODES_RESOURCE_ID}
az role assignment create --role "Virtual Machine Contributor" --assignee ${KUBELET_IDENTITY_ID} --scope ${NODES_RESOURCE_ID}
Then create a user-assigned identity and assign the Monitoring Reader role to the identity.
Step 1. Create a new identity
export IDENTITY_NAME=<identity name>
export NODE_RESOURCE_GROUP="$(az aks show -g ${CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP} -n ${CLUSTER_NAME} --query nodeResourceGroup -o tsv)"
az identity create -g ${NODE_RESOURCE_GROUP} -n ${IDENTITY_NAME}
Step 2. Create a new role assignment for read-only access
export IDENTITY_CLIENT_ID=$(az identity show -g ${NODE_RESOURCE_GROUP} -n ${IDENTITY_NAME} --query clientId -otsv)
export NODES_RESOURCE_ID=$(az group show -n ${NODE_RESOURCE_GROUP} -o tsv --query "id")
az role assignment create --role "Monitoring Reader" --assignee ${IDENTITY_CLIENT_ID} --scope ${NODES_RESOURCE_ID}
Appendix B: Enabling Azure Active Directory Pod-managed Identities (preview version)
Please follow Use Azure Active Directory pod-managed identities in Azure Kubernetes Service (Preview) and create a pod identity that has the "Monitoring Reader" role in the “cloudnatix” namespace.
Step 1. Register the EnablePodIdentityPreview
az feature register --name EnablePodIdentityPreview --namespace Microsoft.ContainerService
az provider register -n Microsoft.ContainerService
Step 2. Install the aks-preview Azure CLI
az extension add --name aks-preview
az extension update --name aks-preview
Step 3. Update an existing AKS cluster with Azure CNI to include pod-managed identity.
export AKS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP=<resource group name of your AKS cluster>
export AKS_CLUSTER_NAME=<your AKS cluster name>
az aks update -g ${AKS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP} -n ${AKS_CLUSTER_NAME} --enable-pod-identity
Or create a new AKS cluster if you haven’t.
az group create --name ${AKS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP} --location eastus
az aks create -g ${AKS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP} -n ${AKS_CLUSTER_NAME} --enable-pod-identity --network-plugin azure
A kubeconfig can be obtained by the following command:
az aks get-credentials --resource-group ${AKS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP} --name ${AKS_CLUSTER_NAME}
Step 4. Create an identity
export IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP="myIdentityResourceGroup"
az group create --name ${IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP} --location eastus
export IDENTITY_NAME="application-identity"
az identity create --resource-group ${IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP} --name ${IDENTITY_NAME}
export IDENTITY_CLIENT_ID="$(az identity show -g ${IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP} -n ${IDENTITY_NAME} --query clientId -otsv)"
export IDENTITY_RESOURCE_ID="$(az identity show -g ${IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP} -n ${IDENTITY_NAME} --query id -otsv)"
Step 5. Assign a read-only role to the identity.
export NODE_GROUP=$(az aks show -g $AKS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP -n $AKS_CLUSTER_NAME --query nodeResourceGroup -o tsv)
export NODES_RESOURCE_ID=$(az group show -n $NODE_GROUP -o tsv --query "id")
az role assignment create --role "Monitoring Reader" --assignee "$IDENTITY_CLIENT_ID" --scope $NODES_RESOURCE_ID
Step 6. Create a pod identity in the “cloudnatix” namespace.
export POD_IDENTITY_NAME="cloudnatix-pod-identity"
export POD_IDENTITY_NAMESPACE="cloudnatix"
az aks pod-identity add --resource-group ${AKS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP} --cluster-name ${AKS_CLUSTER_NAME} --namespace ${POD_IDENTITY_NAMESPACE} --name ${POD_IDENTITY_NAME} --identity-resource-id ${IDENTITY_RESOURCE_ID}
Appendix C: Enabling Workload Identity in AKS
Please follow https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/workload-identity-deploy-cluster to enable workload identity and create a managed identity has the "Monitoring Reader" role for the cluster-watcher service account in the cloudnatix namespace.
Step 1. Update an existing AKS cluster to enable workload identity
export AKS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP=<resource group name of your AKS cluster>
export AKS_CLUSTER_NAME=<your AKS cluster name>
az aks update -g "${AKS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP}" -n "${AKS_CLUSTER_NAME}" --enable-oidc-issuer --enable-workload-identity
Step 2. Create a managed identity
export IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP="myIdentityResourceGroup"
az group create --name ${IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP} --location eastus
export IDENTITY_NAME="cloudnatix-cluster-watcher-identity"
az identity create --resource-group ${IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP} --name ${IDENTITY_NAME}
export IDENTITY_CLIENT_ID="$(az identity show -g ${IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP} -n ${IDENTITY_NAME} --query clientId -otsv)"
Step 3. Assign a read-only role to the identity.
export NODE_GROUP=$(az aks show -g $AKS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP -n $AKS_CLUSTER_NAME --query nodeResourceGroup -o tsv)
export NODES_RESOURCE_ID=$(az group show -n $NODE_GROUP -o tsv --query "id")
az role assignment create --role "Monitoring Reader" --assignee "$IDENTITY_CLIENT_ID" --scope $NODES_RESOURCE_ID
Step 4. Establish federated identity credential trust
export FEDERATED_IDENTITY_CREDENTIAL_NAME=cloudnatix-cluster-watcher-federated-identity
export AKS_OIDC_ISSUER="$(az aks show -g "${AKS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP}" -n "${AKS_CLUSTER_NAME}" --query "oidcIssuerProfile.issuerUrl" -o tsv)"
az identity federated-credential create \
--name ${FEDERATED_IDENTITY_CREDENTIAL_NAME} \
--identity-name "${IDENTITY_NAME}" \
--resource-group "${IDENTITY_RESOURCE_GROUP}" \
--issuer "${AKS_OIDC_ISSUER}" \
--subject system:serviceaccount:"cloudnatix":"cluster-watcher" \
--audience api://AzureADTokenExchange
Appendix D: Setting up an IAM Role for the CloudNatix Service Account in EKS clusters
If a cluster uses IAM roles for service accounts, the ec2:Describe* permission or the AmazonEC2ReadOnlyAccess policy needs to given to the cluster-watcher service account in the cloudnatix namespace.
Here is an example command for creating an IAM role and associating with the service account.
CLUSTER=<your cluster name>
eksctl create iamserviceaccount \
--name cluster-watcher \
--namespace cloudnatix \
--cluster "${CLUSTER}" \
--role-name CloudNatixClusterController \
--attach-policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ReadOnlyAccess \
--approve
The service account created by the above command needs to be deleted so that CloudNatix will be able to create it later from its own Helm chart.
kubectl delete serviceaccount cluster-watcher -n cloudnatix
Appendix E: Enabling GKE Workload Identity and Configuring a service account
This section explains how to enable GKE Workload Identity Federation to give sufficient permissions to CloudNatix.
The following steps are based on the GKE guide "Authenticate to Google Cloud APIs from GKE workloads".
First, enable Workload Identity Federation for your cluster.
For Autopilot clusters, it's enabled by default.
For existing Standard clusters, type the following commands to enable it:
CLUSTER_NAME=<your cluster name>
REGION=<region>
PROJECT_ID=<your project ID>
gcloud container clusters update "${CLUSTER_NAME}" \
--region="${REGION}" \
--workload-pool="${PROJECT_ID}.svc.id.goog"
NODE_POOL=<node pool>
gcloud container node-pools update "${NODE_POOL}" \
--cluster="${CLUSTER_NAME}" \
--region="${REGION}" \
--workload-metadata=GKE_METADATA
Then, create a service account that grants the compute.viewer role and the container.clusterViewer role to cluster-watcher in the cloudnatix namespace.
SERVICE_ACCOUNT=cloudnatix
gcloud iam service-accounts create "${SERVICE_ACCOUNT}" \
--project="${PROJECT_ID}"
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding "${SERVICE_ACCOUNT}@${PROJECT_ID}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:${PROJECT_ID}.svc.id.goog[cloudnatix/cluster-watcher]"
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding "${PROJECT_ID}" \
--member "serviceAccount:${SERVICE_ACCOUNT}@${PROJECT_ID}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role roles/compute.viewer
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding "${PROJECT_ID}" \
--member "serviceAccount:${SERVICE_ACCOUNT}@${PROJECT_ID}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role roles/container.clusterViewer
Now, it's ready to install CloudNatix to the cluster. Please specify the service account cloudnatix@<Project ID>.iam.gserviceaccount.com when the cnatix clusters configure command asks for.
Appendix F: Set up user profile in OCI
Step 1. Create a group
To create an OCI group, run the following command:
oci iam group create \
--description "Group for cloudnatix" \
--name "CloudNatix"
Step 2. Set up a policy
First create a policy file in json format, e.g.:
cat oci_global_cluster_watcher.json
{
"compartmentId": "ocid1.tenancy.oc1..***",
"description": "Cloudnatix read-only policy",
"name": "CloudNatix",
"statements": [
"Allow group 'Default'/'CloudNatix' to read all-resources in tenancy"
]
}
Then create the policy by running the following command:
oci iam policy create \
--from-json file://oci_global_cluster_watcher.json
Step 3. Set up a user
To create an OCI user, run the following command:
oci iam user create \
--description "User for cloudnatix" \
--name "tenant-name@cloudnatix.com" \
--email "tenant-name@cloudnatix.com"
Then, add the user to the group created above by running the following command:
oci iam group add-user \
--group-id ocid1.group.oc1..*** \
--user-id ocid1.user.oc1..***
You may also create the user, group and policy through OCI web portal.
Appendix G: Configure Workload Identity in OKE
OKE Enhanced clusters allow you to grant permissions with workload identity. The following is a sample policy, which allows CloudNatix Cluster Controller to have read-only access to OCI resources in OKE clusters.
$cat oci_statements.json
{
"compartmentId": "ocid1.tenancy.oc1..****",
"description": "CloudNatix workload policy",
"name": "cloudnatix",
"statements": [
"Allow any-user to read all-resources in tenancy where all {request.principal.type = 'workload',request.principal.namespace = 'cloudnatix',request.principal.service_account = 'cluster-watcher'}"
]
}
$oci iam policy create --from-json file://oci_statements.json
Appendix H: Deploying a Cluster Controller Helm Chart via a CI/CD Pipeline
Suppose that we run cnatix clusters configure and generate a Helm chart for cluster my-cluster. The Helm chart is generated under ~/.cnatix/cluster-configs/my-cluster/ccoperator.
my-cluster/
├── ccoperator
│ ├── Chart.yaml
│ ├── templates
│ │ ├── base.yaml
│ │ └── secrets.yaml
│ └── values.yaml
├── ...
Please see Appendix I for what each of the fields in the Helm values means.
Please take the following steps when checking in a Helm chat to a repository:
- Remove
ccoperator/templates/secret.yaml - Remove
apiKeyanddockerconfigjsonfromccoperator/values.yaml
These contain secrets that shouldn’t be checked into a repository. The following is the content of secret.yaml.
apiVersion: v1
data:
.dockerconfigjson: {{ .Values.dockerconfigjson }}
kind: Secret
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/created-by: cloudnatix
name: docker-pull-secret
type: kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/created-by: cloudnatix
name: {{ .Release.Name }}-secret
stringData:
api-key: {{ .Values.apiKey }}
type: Opaque
The former secret is to pull Docker images. The latter secret is to create a JWT token embedded in API calls to Global Controller. The two secrets still need to be created in a target cluster. The actual way to create the secrets depends on a customer (e.g., helm-secrets, Hashicorp Vault).
When configuring a CI/CD pipeline for multiple clusters, the generated template files can be reused for the clusters. Only values.yaml needs to be updated.
The chart is also available at https://charts.cloudnatix.com. Here is an example command to pull the chart.
helm repo add cloudnatix https://charts.cloudnatix.com
helm repo update
helm pull cloudnatix/ccoperator
Appendix I: Helm Values Definition
This section describes the definitions of the Helm values.
Secrets
These values specify the secrets used to make API calls to CloudNatix as well as pull docker image.
apiKey: ""
dockerconfigjson: ""
The value for apiKey is obtained with cnatix iam users get-apikey.
The value for dockerconfigjson is obtained with the following command:
API_KEY=<Your API key>
cat << EOF | base64 --wrap=0
{
"auths": {
"registry.cloudnatix.com": {
"auth": "${API_KEY}"
}
}
}
EOF
Please see Appendix H if you don't want to check-in these values in source code repositories.
Per-Cluster Configuration
These values specify per-cluster configuration.
clusterName: ""
csp: ""
orgUuid: ""
aws:
region: ""
vpcId: ""
accountId: ""
iamRole: ""
iamExternalId: ""
azure:
subscriptionId: ""
location: ""
resourceGroup: ""
clusterResourceGroup: ""
vnetName: ""
podIdentityName: ""
aadPodIdentity:
resourceId: ""
clientId: ""
gcp:
projectId: ""
region: ""
zone: ""
serviceAccount: ""
baremetal:
datacenter: ""
network: ""
username: ""
oci:
clusterOcid: ""
compartmentOcid: ""
fingerprint: ""
region: ""
tenancyName: ""
tenancyOcid: ""
userOcid: ""
userPrivateKey: ""
useWorkloadIdentity: false
clusterName is the name of the Kubernetes cluster.
orgUuid is the UUID of the org where the cluster belongs. If it is empty, the cluster belongs to the root org.
csp is set to one of aws, azure, gcp, oci, or baremetal. For each CSP, additional parameters need to be set.
aws.iamRole and aws.iamExternalId must be set if the cluster enables IAM roles for service accounts. Please see Appendix D for the details.
CCOperator and Component Versions
These values specify the CCOperator version and the installation parameters for the components installed by CCOperator.
ccOperatorVersion: (e.g., "0.293.0")
distributionVersion: "21.2"
channelName: stable
autoUpgrade: true
componentSpecs: {}
isPrometheusInstallSkipped: false
isVpaPreinstalled: false
ccOperatorVersion specifies the CCOperator version. Please see Release Notes for the latest available version.
distributionVersion and channelName control the components versions. 21.2 and stable are the default values to be set.
autoUpgrade controls whether all components are automatically updated or not. componentSpecs specifies individual component versions. Please visit this page for details.
isPrometheusInstallSkipped is set to true if CloudNatix should not install Prometheus. This is set to true when the cluster already has Prometheus or K8s Metrics API is used for metrics collection.
isVpaPreinstalled is set to true if CloudNatix should not install VPA.
Metrics Collection Configuration
These values specify how CloudNatix Cluster Controller collects performance metrics from K8s clusters.
useK8sMetrics: false
prometheusUrl: ""
isKubeSystemManaged: false
We currently support two ways to collect performance metrics: Prometheus and K8s Metrics API.
- To use K8s Metrics API, set
useK8sMetricstotrue. - To use Prometheus installed by CloudNatix, set
useK8sMetricstofalseand setprometheusUrlto an empty string. - To use Prometheus that already exists in the cluster, set
useK8sMetricstofalseand setprometheusUrlto the URL of the existing Prometheus instance.
isKubeSystemManaged is set to true when the kube-system namespace of the cluster is managed by CSP and CloudNatix is not able to access (e.g., GKE autopilot clusters).
Other Miscellaneous Configuration
These values specify other miscellaneous configuration.
scrubSensitiveData: false
bindClusterAdminRole: true
clusterOwnerRole: ""
prometheusRemoteWriteDomain: ""
reportToDatadog: ""
scrubSensitiveData is set to true if container arguments and environment variables are dropped when CloudNatix Cluster Controller sends workload metadata information to Global Controller.
prometheusRemoteWriteDomain is set when Prometheus metrics are sent to a Grafana instance managed by CloudNatix. An example value is api.monitoring.<tenant-name>.cloudnatix.com.
reportToDatadog is set to none to disable Datadog integration. Please see the Datadog integration page for details.
Please see Appendix J for bindClusterAdminRole and clusterOwnerRole.
Additional Specs for Deployments and Pods
These values specify additional specs added to deployments and pods.
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
deployment: {}
podTemplate: {}
finalizers:
- cloudnatix.com/ccoperator
nodeSelector and tolerations specify node selectors and tolerations that are added to the CCOperator pods and other pods created by CCOperator.
deployment and podTemplate are used to specify additional labels and annotations that are set to the deployments and pods. Here is an example values:
deployment:
labels:
- key: value
annotations:
- key: value
podTemplate:
labels:
- key: value
annotations:
- key: value
The finalizers controls the behavior of uninstallation. If set, the ccoperator pod deletes all resources created by CloudNatix when CloudNatix is uninstalled from the cluster.
Parameters for Internal Use
These parameters control the internal mechanism of ccoperator and experimental features. These do not need to be changed.
globalControllerDomainName: cloudnatix.com
ccOperatorRegistry: registry.cloudnatix.com/cloudnatix/ccoperator
healthUpdateInterval: 1m0s
installLoopInterval: 1m0s
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 300
cnatixInstallMode: FullAccess
componentsVersions: {}
Appendix J: Installing CloudNatix without Binding the cluster-admin Role
By default the ccoperator deployment and clusteragent deployment have the cluster-admin role. This is necessary to give the cluster-admin role to cluster-owner org admins who access Kubernetes clusters with CloudNatix Secure Sessions.
If you do not want to bind the cluster-admin role to the deployments, please set the following in the values.yaml:
bindClusterAdminRole: false
clusterOwnerRole: (admin|edit|view)
clusterOwnerRole controls the role that is given to cluster-owner org admins.
Appendix K: Installing the CloudNatix CLI without login
We typically suggest using the CloudNatix web UI to download the CLI, but you can also do it without direct access to the UI. To perform this installation you will need JQ. If you do not already have it you can find the download link from the project github.
After JQ is installed, run the following commands to download the CLI and install it:
For Linux:
curl "https://api.cloudnatix.com/v1/artifact-download-url" -G \
--data-urlencode "name=cli" \
--data-urlencode "distribution_version=21.2" \
--data-urlencode "channel=stable" \
--data-urlencode "os_arch=linux-amd64" \
| jq '.downloadUrl' --raw-output \
| xargs curl --output cnatix
sudo mv cnatix /usr/local/bin
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/cnatix
cnatix
For macOS:
curl "https://api.cloudnatix.com/v1/artifact-download-url" -G \
--data-urlencode "name=cli" \
--data-urlencode "distribution_version=21.2" \
--data-urlencode "channel=stable" \
--data-urlencode "os_arch=darwin-amd64" \
| jq '.downloadUrl' --raw-output \
| xargs curl --output cnatix
sudo mv cnatix /usr/local/bin
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/cnatix
cnatix

